Most Common Grammar Mistakes and How to Fix Them Quickly (+ Free Tools)


Whether you’re a beginner or a native speaker, the English language can be confusing and challenging.
To save you from poor grammar, we‘ve listed down the most common grammatical errors to help you write your best error-free work. It comes with some handy examples and tips so you can avoid these writing mistakes and fix them quickly.
Plus, we’ve also rounded up the best free tools to check these common grammar mistakes and improve your overall writing to be clearer, more accurate, and more professional.
One of the most common grammar mistakes is the comma splice. This happens when you use a comma in two complete sentences—commonly known as independent clauses—without placing a suitable join between them.
A comma splice is a common kind of comma mistake because the comma can’t stand on its own to make one grammatical sentence out of the two independent clauses.
There are three ways to recognize and fix this grammatical error. You can simply rewrite the two independent clauses into two separate sentences, switch the comma to a semicolon, or add either coordinating conjunctions or subordinating conjunctions.
Quick Fix #1: Rewrite the clauses into two sentences.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Mariah went to the drugstore, she bought pain relievers. | Mariah went to the drugstore. She bought pain relievers. |
Quick Fix #2: Add either a coordinating conjunction or subordinating conjunction.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| I am sleepy, my report is due today. | I am sleepy, but my report is due today. |
Quick Fix #3: Switch the comma to a semicolon.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| He had class this morning, he woke up at noon. | He had class this morning; he woke up at noon. |
A closely related grammatical error to a comma splice is the run-on sentence. It occurs when two or more independent clauses are joined without any punctuation mark at all.
Rectifying a run-on sentence is no different from correcting a comma splice. Each independent clause must be separated from other independent clauses with punctuation marks like a comma, period, semicolon, and em dash.
The most common error writers make with a run-on sentence is neglecting to use a comma before a coordinating conjunction like and, but, or.
Realizing this gap in their writing skills, some authors or students who handle many writing assignments in college consider a “write my essay” option from outsourced specialists. (At a minimum, they ask to proofread their text or edit it by a professional writer, though such a tiny error is easy to fix.)
Quick Fix #1: Add a comma before a coordinating conjunction.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Pablo Picasso used color as an expressive element in his paintings but he relied on drawing rather than subtleties of color to create form and space. | Pablo Picasso used color as an expressive element in his paintings, but he relied on drawing rather than subtleties of color to create form and space. |
Quick Fix #2: Rewrite the sentence as two separate sentences.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| He loves to play computer games he would play daily if he had time. | He loves to play computer games. He would play daily if he had time. |
Quick Fix #3: Use subordinating conjunction.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| I am bored with this movie the plot is too predictable. | I am bored with this movie because the plot is too predictable. |
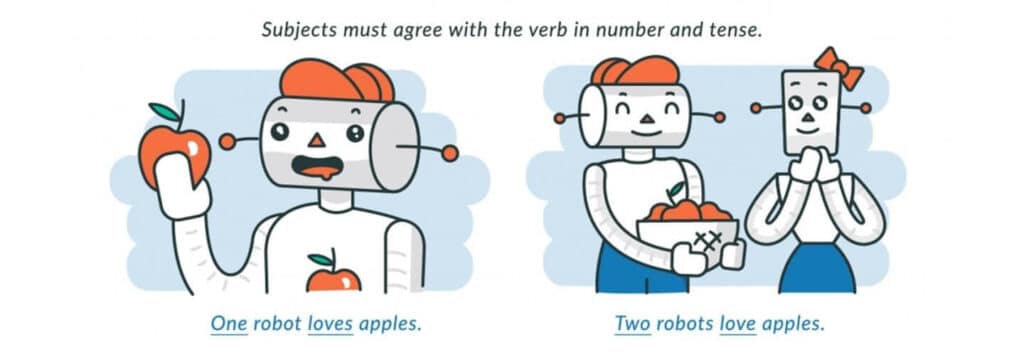
Subject-verb agreement denotes that a subject and its verb must be both singular or both plural:
Source: Albert.
In contrast, subject-verb disagreement arises when the subject of your sentence and its corresponding verb do not match in terms of singularity or plurality. It’s one of the most common grammar mistakes that can be confusing to the reader.
In English, irregular verbs and compound subjects make subject-verb agreement somewhat tricky. Irregular verbs, like those above, must be memorized, but compound subjects follow a simple rule—they are plural. See below for an example using the compound subject Jane and Mark.
Quick Fix #1: Singular subjects joined by the word and are typically plural.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Both the manager and the employees prefers an output-based approach. | Both the manager and the employees prefer an output-based approach. |
Quick Fix #2: Indefinite pronouns (someone, anyone, anybody, somebody, nobody, no one, one, either, neither) generally take a singular verb.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Nobody want to be lonely. | Nobody wants to be lonely. |
Quick Fix #3: Plural nouns (economics, athletics, politics, news, measles, mumps) take a singular verb.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Economics seek to analyze and describe the production, distribution, and consumption of wealth. | Economics seeks to analyze and describe the production, distribution, and consumption of wealth. |
Quick Fix #4: Uncountable nouns are considered singular and may take only singular verbs.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The furniture in this house need to be replaced. | The furniture in this house needs to be replaced. |
Quick Fix #5: When used in sentences, the titles of books, plays, poems, movies, and so on take singular verbs.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Samuel H. Young’s Psychic Children are both disturbing and entertaining to read. | Samuel H. Young’s Psychic Children is both disturbing and entertaining to read. |
Have you come across words that are spelled the same, but have distinct meanings? How about words that are spelled differently, but sound identical? We call them homophones, homographs, or homonyms. Let’s have a look at their subtle differences below:

Here are some of the most commonly confused words that you should study to avoid grammar mistakes and find the right word the next time your write:
Advice vs. Advise
Advice is an opinion or recommendation offered as a guide to action. Advise means to recommend, or to give information to someone.
Advice vs. Advise: Lily advised Rose to consult a doctor immediately. Rose took Lily’s advice seriously.
Affect vs. Effect
Affect is make a difference to. Effect means the outcome of an event or situation that created a change.
Affect vs. Effect: While the researcher didn’t see how planning affected his project, the negative effects soon became evident.
Lose vs. Loose
Lose is to fail to win or to misplace. Loose means not tight.
Lose vs. Loose: She always tends to lose her loose-fitting shorts.
Their vs. There vs. They’re
Their is the possessive pronoun of they. There means place. They’re is a contraction of “they are.”
Their vs. There vs. They’re: Their cat is over there trying to steal food at the grocery store. They’re not the most responsible pet owners.
Your vs. You’re
Your is the possessive form of you. You’re is a contraction of “you are.”
Your vs. You’re: You’re so stubborn. I told you not to waste your money.
Here are other confusing word pairs for you to study:
Sentence fragments are also among the most common grammar mistakes worldwide. A sentence fragment is an incomplete thought or line that looks like a sentence but lacks the structure to form a complete sentence.
In a conversation, sentence fragments are no big deal. However, you should generally avoid them in formal writing as they are a form of grammatical error.
While there are many ways to end up with sentence fragments, they are simply a result of one of the three grammar mistakes:
Quick Fix #1: Add the missing part (subject or verb) to complete the thought.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Singing his new Christmas single. | Corey is singing his new Christmas single. |
Quick Fix #2: Join the fragment to a nearby complete sentence.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The current school policy on social distancing is incomplete as it stands. Which is why we urge the student council to propose new amendments immediately. | Because the current school policy on social distancing is incomplete as it stands, we urge the student council to propose new amendments immediately. |
A modifier is a word, phrase, or clause that describes or qualifies another word or word group. When the modifier is not clearly stated in the sentence, it is called a dangling modifier. The modifier sits independently, modifying nothing.
When a sentence doesn’t obviously state the subject being modified, the introductory phrase turns into a dangling modifier. Sentences with dangling modifiers can sound awkward, ridiculous, or incoherent. Often this error is a result of the main clause written in the passive voice like this below:
In the above sentence, the intended target of the modifier is missing. Because a dog crossing appears where the subject should be, the sentence now implies that a dog crossing the road was driving to the mall. If the sentence is written in the active voice, it’s clear who is supposed to do what just like this:
Quick Fix #1: Leave the modifier as it is and then rewrite the main clause so that it starts with the subject being modified.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Thirsty after a dance rehearsal, my bottled water was quickly drunk. | Thirsty after a dance rehearsal, I quickly drank my bottled water. |
Quick Fix #2: Include the subject in the introductory phrase, leaving the main clause as it is.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Without knowing his birthdate, it was hard to know his age. | Because Viktor did not know his birthdate, it was hard to know his age. |
A compound sentence consists of two or more independent clauses, typically joined by a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, or so) and a comma or by a semicolon alone. It’s best used to combine two or more complete sentences and related sentences into a single, unified one.
When a compound sentence is joined by a coordinating conjunction, a missing comma is often one of the most common grammar mistakes that people make. The rule is pretty straightforward. A comma before the coordinating conjunction must be present to help the reader see the boundary between the separate independent clauses.
Alternatively, if there’s no coordinating conjunction, a semicolon can be added between the clauses. This way, the sentence is still grammatically correct.
Quick Fix #1: Add a comma before the introductory word, phrase, or clause.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The archeologist lost his map but he still found the excavation site. | The archeologist lost his map, but he still found the excavation site. |
Quick Fix #2: If there’s no coordinating conjunction, place a semicolon between each clause.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Paris is the most romantic city I plan to spend a month there next week. | Paris is the most romantic city; I plan to spend a month there next week. |
Inconsistent verb tense is another one of the most common grammar mistakes. When the verb tense is inconsistent, it’s unclear to the reader when the action you are describing is happening. You want to avoid having one time period being expressed in two different tenses.
In creative writing, tenses may be used inconsistently to add dramatic effect. However, in academic and professional writing, it’s important to use verb tense consistency, so that readers can follow the progress of ideas and arguments easily.
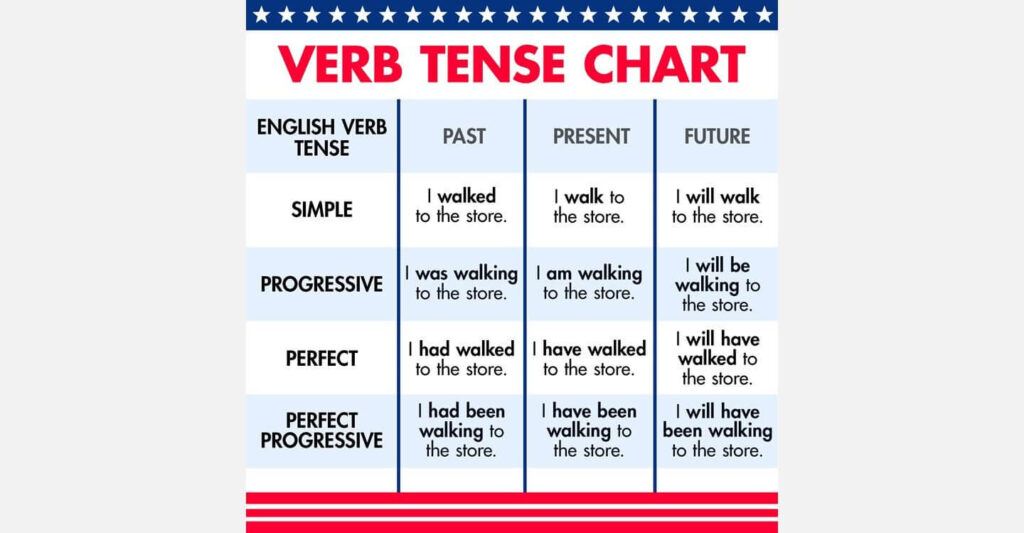
Here’s a brief review of the verb tenses.
Source: YourDictionary.
Do not shift tenses between sentences unless there is a good reason to switch tenses. Take a look at how the verb tenses shift in the sentence below:
The action word in the first sentence above is written in the past tense. However, the verb in the second sentence suddenly shifts to the present tense. This shift in verb tense denotes inconsistent periods.
But verb-tense shifts are not always incorrect. They are still extremely useful to inform the readers of the different times at which things occur. To illustrate, let’s analyze this sentence:
The verbs “walked” and “was sitting” tell us slightly different things about when those actions took place. The door was only opened once in the past, but the verb “was standing” tells us that Rory was already sitting around the corner when the door opened. She may or may not also continue sitting there even after the door opens.
Quick Fix #1: Do not shift from one tense to another if the time frame for each action or state is the same.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The professor explains the formula to the students who asked questions during the class. | The professor explains the formula to the students who ask questions during the class. |
Quick Fix #2: Do shift tense to indicate a change in the time frame from one action or state to another.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The sisters love their new dollhouse, which they assemble on their own. | The sisters love their new dollhouse, which they assembled on their own. |
The voice of a verb may be either active or passive in a sentence. When a sentence contains two or more verbs, both verbs should maintain the same voice.
Inappropriate shifts in verb voice can be confusing to the reader. As a general rule, active voice is preferred over passive voice. Active sentences in active voice are easier to understand. In some cases, passive voice may be a better option, but only when the subject is unknown, unwanted, or not needed in the sentence.
Quick Fix #1: Maintain the same verb voice in a sentence.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| The art gallery was preserved by the local government because they realized its money-making potential. | The local government preserved the art gallery because they realized its money-making potential. |
Parallelism in grammar refers to the principle that elements of a sentence that are the same in function should be the same in structure. This can happen at the word, phrase, or clause level. Usually, parallel structures are joined with the use of coordinating conjunctions like “and” or “or.”
Lack of parallelism can happen in a variety of ways. Double-check your sentences to ensure you’re not making these common grammar mistakes:
Quick Fix #1: Make sure phrases joined by coordinating or correlative conjunctions are parallel.
| Incorrect ❌ | Correct ✅ |
|---|---|
| Cosmetic dentistry assists in reclaiming the beauty of your smile and to treat the malformations of your teeth. | Cosmetic dentistry assists in reclaiming the beauty of your smile and treating the malformations of your teeth. |
Quick Fix #2: Ensure all headings and subheadings are parallel with the other headings and subheadings of the same level.
Incorrect ❌
How to Implement a Better Framework
Correct ✅
How to Implement a Better Framework
Whether you’re working writing an important email, crafting a cover letter for your job application, pitching a client project proposal, good writing is your first step to making a big impression.
When the stakes are this high, the risk of committing grammar mistakes is even higher.
Thankfully, the following online grammar checker tools can help you spot and fix grammar errors quickly.
Grammarly has a tool for just about every type of writing need. From individual to corporate accounts, you have access to their English writing assistance technology which works seamlessly across multiple platforms and devices.
If you need to do a quick grammar check, their online Grammar Check tool can scan your text for all types of mistakes (typos, incorrect capitalization, sentence structure, etc.) for free.
For checking longer documents, try installing the Grammarly app available on both Windows and Mac. It also works across apps, documents, and emails.
Alternatively, you can add Grammarly’s browser extensions to offer writing suggestions and grammar corrections on a range of websites, including Google Docs, Medium, and Twitter.
Hemingway App is a writing editor tool that highlights grammar mistakes and suggests an alternative correction. It’s a self-editing tool that helps you polish your writing.

Compared to Grammarly, this app is more focused on improving your writing style. It focuses on fixing common errors like confusing sentence construction, excessive weak adverbs, and overuse of the passive voice.
LanguageTool is a free online proofreading service for English and 20+ other languages. It’s powered by an AI-based technology that examines the style, tonality, and typography of your text and quickly generates context-based suggestions.
Their free Grammar Checker for English tool instantly reviews your text for grammar and style mistakes. It’s compatible with other tools like Word, Google Docs, OpenOffice, and more.
You can also add it as an extension to your favorite browser.
Whether you are a novice, veteran, or native speaker of the English language, always look out for spelling errors. Misspellings can be easily spotted by your readers. If your writing has full of them, this can tarnish your credibility and lead to misinterpretation of your message.
Punctuation is also extremely important. Any misplaced punctuation mark can alter the entire meaning of the sentence. Ensure that you have those punctuation marks in the right places. Whatever you’re writing, it’s also a great idea to read out your sentences aloud. Listening carefully to what you’ve written can help you hear what part of the sentence sounds odd.
No matter how careful and attentive we are while writing, there’s still a significant chance for us to make errors. We are humans, after all. In this case, a grammar checker tool can be a lifesaver.
Today, online tools like Grammarly or Hemingway App can quickly highlight any errors you may have missed. You can save the embarrassment of turning in a work full of grammatical errors.
English is one of the most spoken languages in the world. However, it’s also widely regarded as one of the hardest languages to master. To improve your English skills, reading is fundamental. From novels, online articles, newspapers to magazines, continuous reading can help you with real-life examples of sentences and maybe pick up some slang words and phrases that you can use.
Just like reading, watching movies or television series and listening to music can also help. With this, always make sure to practice what you’ve learned with your face-to-face interaction. The only way you can improve is to put your learning into practice.
With the advent of new communication channels like social media, messaging, and chat apps, we’ve been communicating a lot more in writing. Unlike oral communication, bad grammar in written communication is more unforgivable. Plus, it’s easier to spot grammatical errors too.
Good grammar helps you articulate your message or idea clearly. It’s also the foundation of great writing. With great writing, you can land a job, achieve success in your current career, or relate to your social circle—the possibilities are endless.